Complex networks and time-series tools in nonlinear FSI and VIV
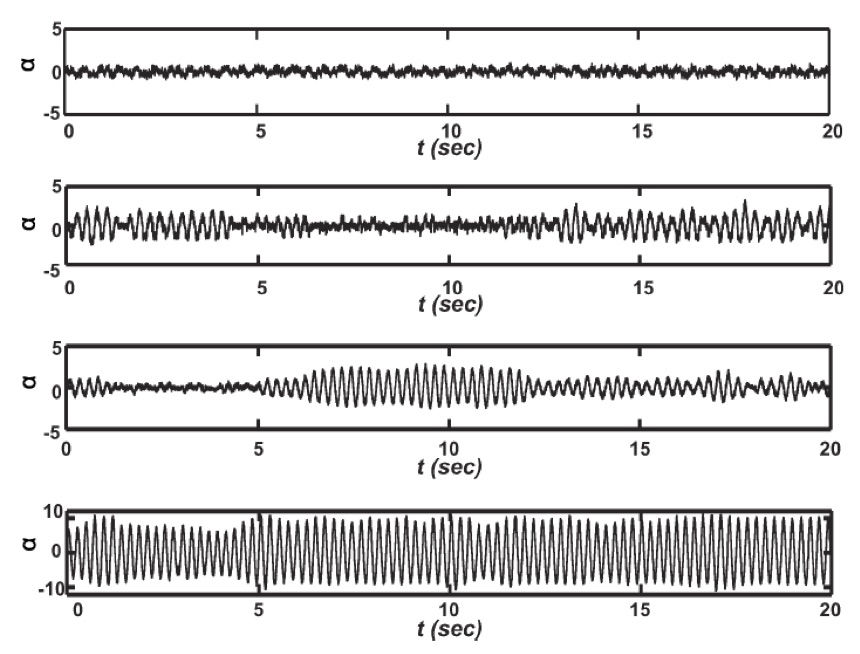
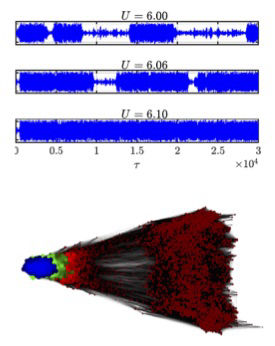
Large order nonlinear multi-physics systems, as in aeroelastic, acousto-elastic, FSI and VIV systems need smart tools to assess their dynamics as classical nonlinear tools are cumborsome and often inconclusive. Response time-series hold the key to their dynamics (reconstructed space-space) and can be utilised to convert to visual tools like complex networks. We have explored recurrence networks, correlation networks and visibility graphs, among others. Figure shows response time series at different flow velocty parameter (U) and recurrence netowrk for one case.
Physics Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) based surrogates in unsteady flow-field of flapping
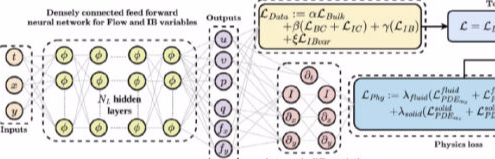
PINNs have been used for hidden physics recovery in the highly vortex dominated fow-fields at low Re around flapping bodies. Immersed-boundary aware frame-work was developed to work with sparse IBM simulation data to identify high resolution velocity and pressure data as hideen physics exercise with good success. We are also interested in high resolution data recovery with zero input on the moving boundary positions, forward problems (with zero data) as well as temporally scarse data under PINNs frameworks. Figure shows a schematic of the architecture of moving boundary aware IBM-PINN (MB-IB-PINN).
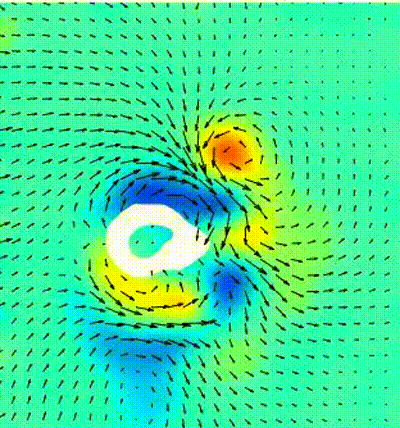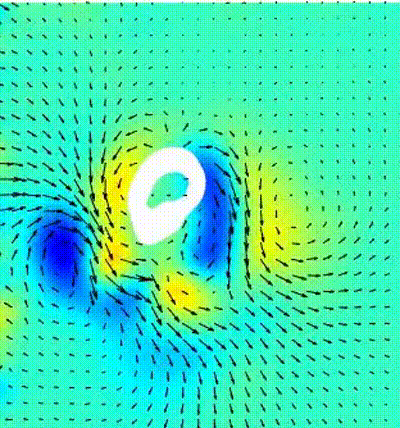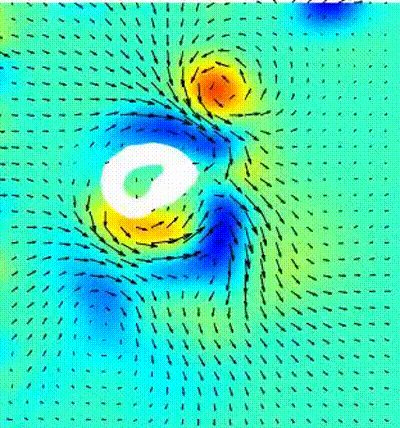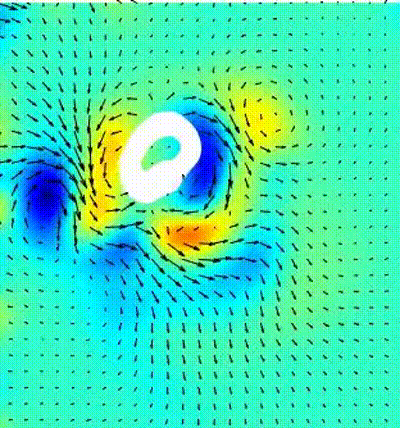
Bio-mimetic propusion with gaits of natural swimmers
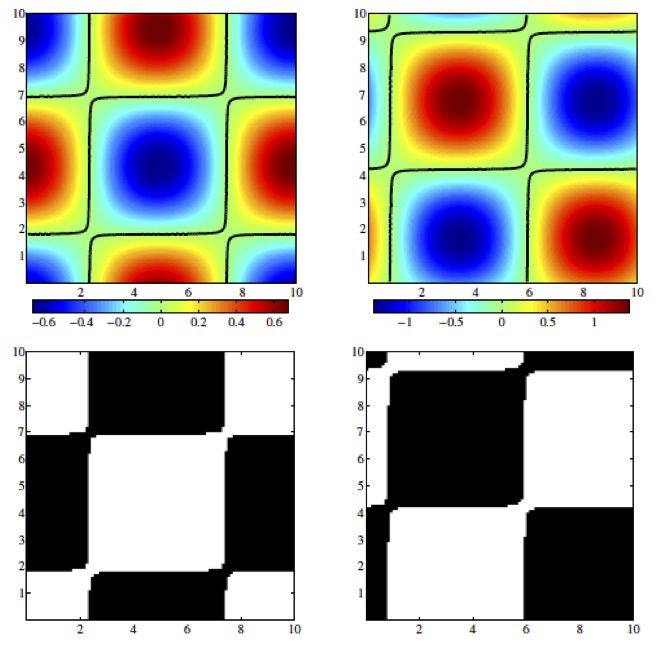
We show samples from our studies of chess-board patterns (bottom frames) modelled as a discrete valued random process and transformed to equivalent Gaussian process (top frames); Gaussian statistics are simpler to deal with. Lot of stochastic modelling and propagation of input randomness through nonlinear large order flow and FSI problems are being done.
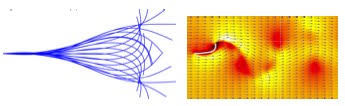
Energy harvesting from flow-induced-vibration
Harvesting energy from flexible deforbale structure using piezoelextric and other smart materials Fluid-structure interaction (FSI) of highly flexible and extremely light weight MAV wings are also of our interest which manifest a very different qualatiative behaviour from that of aircrafts or rotor blades.
Classical as well as stall induced aeroelastic models are being studied in this regard. Flow induced vibrations of bluff bodies assume a significant practical interest due to the wide ranging application of this problem. Cylinder under vortex induced vibration encounteres large amplitude oscilaltions during the `lock-in' zone, a parametric regime where the frequency of vortex shedding locks onto the structural natural frequency.Experimental studies are also conducted in the low speed wind tunnel .