Hydrogen Energy & Fuel Cell
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells using hydrogen as fuel, are considered as the potential power source for a variety of applications such as distributed stationary power generation systems and automobiles. A PEM fuel cell directly converts the chemical energy of the fuel into electricity thus providing higher energy conversion efficiency. PEM fuel cells cause no pollution at the point of operation and have no moving parts thus increasing the reliability and lifetime of the equipment. Commercialization of the technology however demands addressing a number of engineering challenges such as ensuring uniform reactant distribution, efficient water management and effective heat removal.
Our research group focuses on addressing some of these challenges through theoretical as well as experimental studies.
- The importance of designing the flow distributors such that product water is retained inside the fuel cell.
- Self-humidified operation by eliminating the need for external humidification systems.
- Adverse effects of Copper corrosion in current collectors on the performance of PEM Fuel cells.
- Enhancing water management in a PEM Fuel Cell with Super-hydrophobic flow fields on the Cathode side.
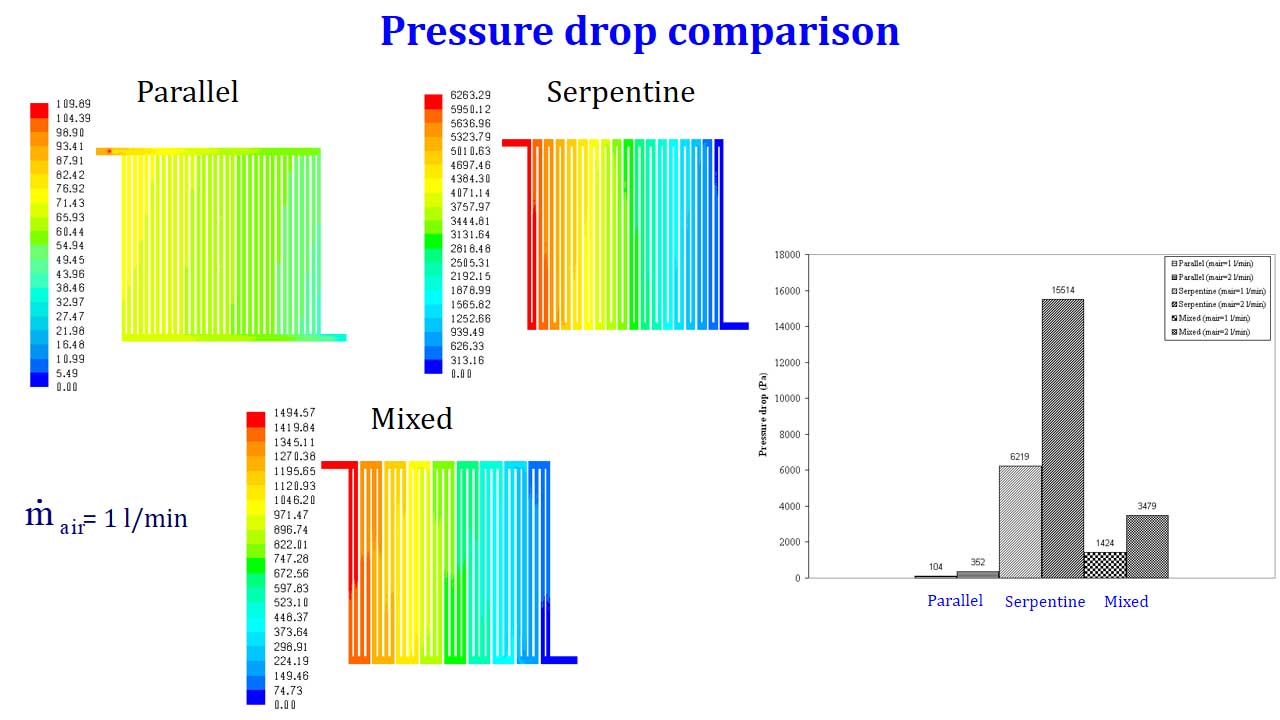
Pressure drop comparison
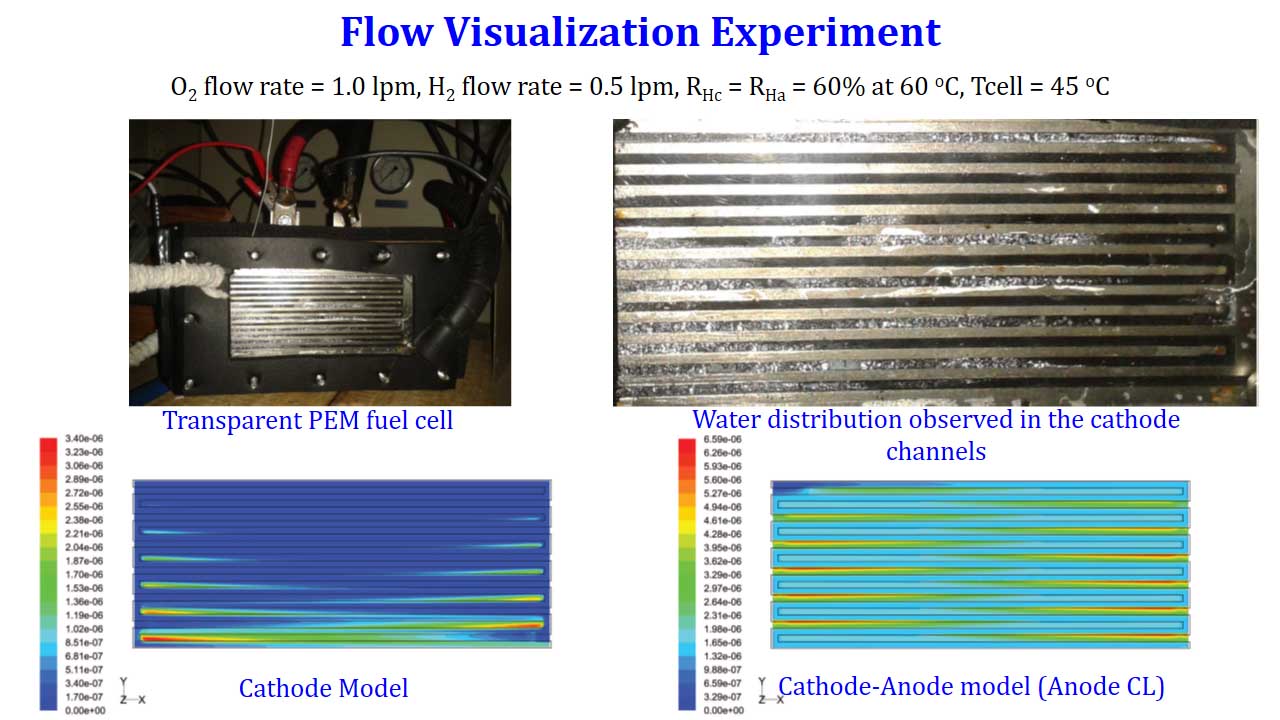
Flow visualization experiment
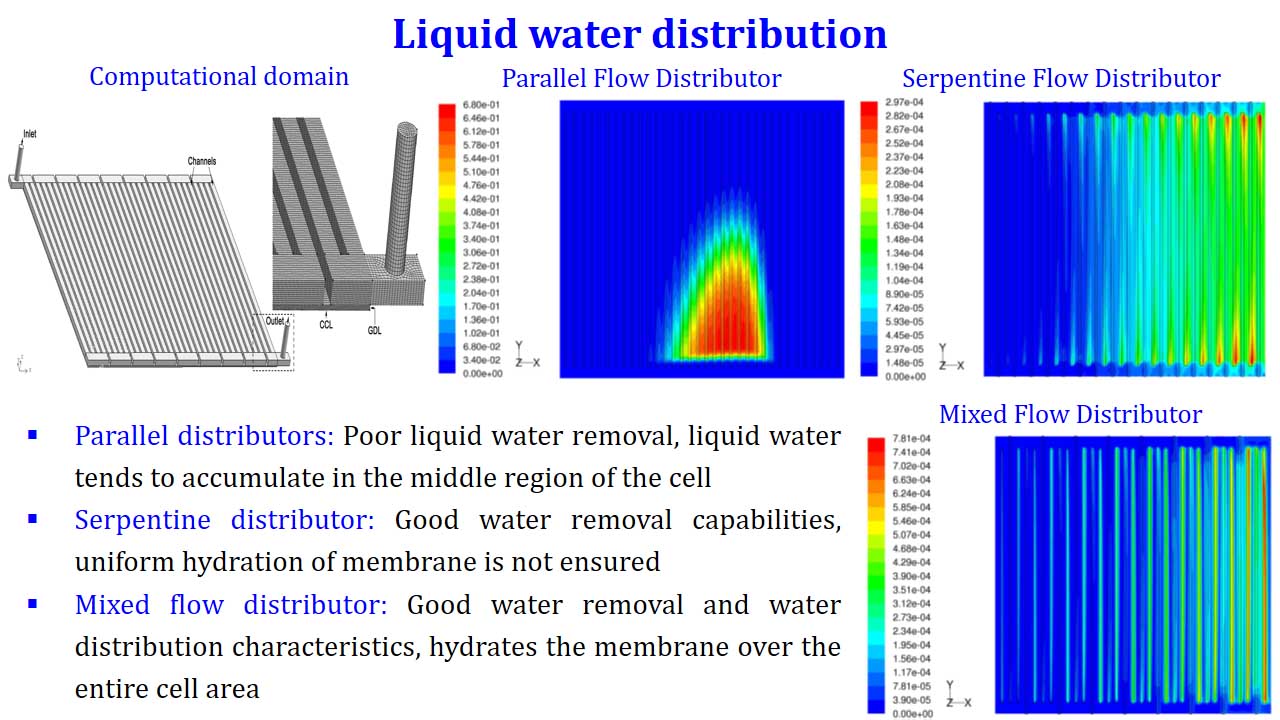
Liquid water distribution
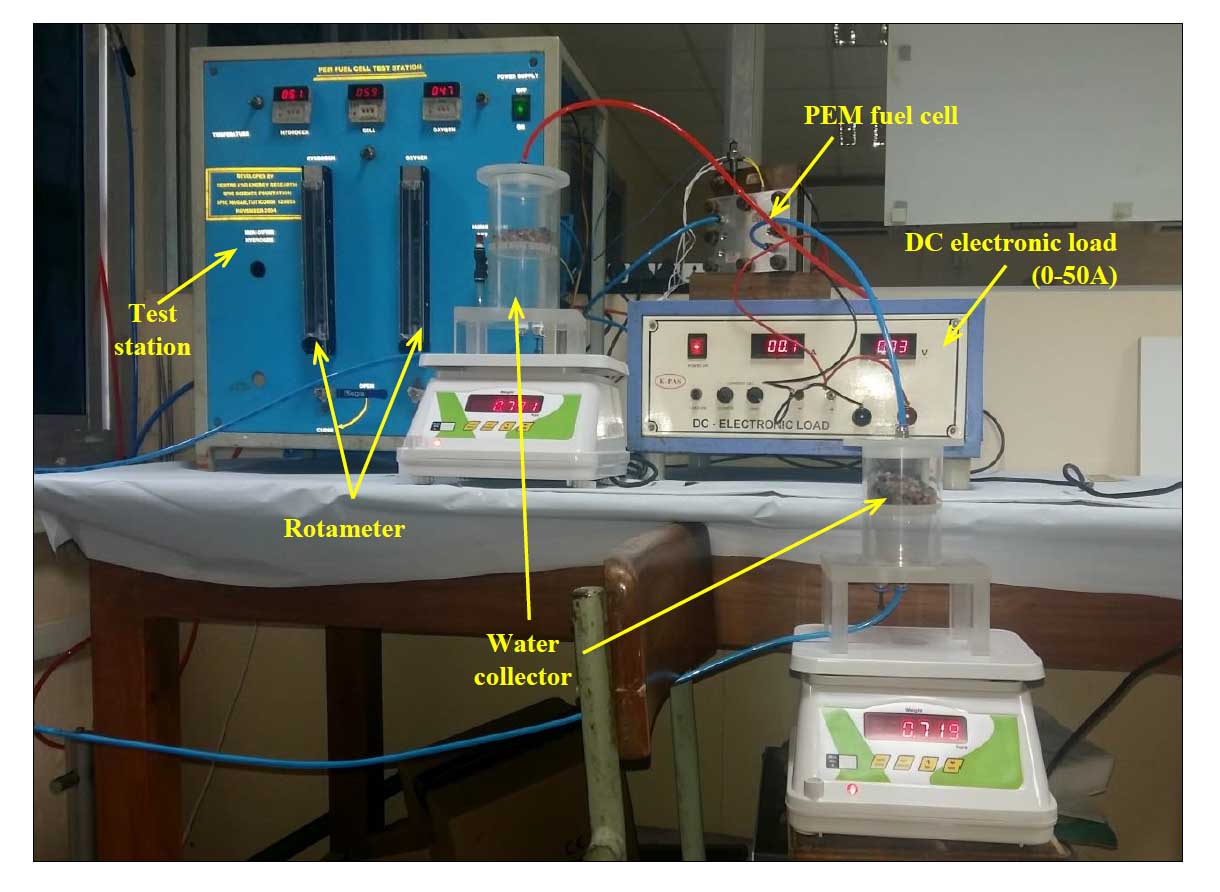
Experimental Setup